Ashley Lepham November 8, 2022
CHARLOTTE (Crater Hydrogen and Regolith Laboratory on Technical Terrain Environments) is a 6-legged rover developed by ASU students at the Luminosity Lab as a part of one of NASA’s BIG Idea Challenges – Extreme Terrain Mobility Challenge. The Interplanetary Lab provided both engineering and environmental testing support for the Luminosity team. From June to October 2022, the Interplanetary Lab accomplished four major tasks for CHARLOTTE: 1) the design and construction a lunar sandbox capable of imitating lunar gravity and containing lunar regolith simulant to test CHARLOTTE’s traction and dust ingress, 2) the design and construction of a structure to conduct abrasion testing on CHARLOTTE’s Medium Voltage Direct Current (MVDC) cable, 3) thermal cycling tests on CHARLOTTE’s carapace, 1 DOF leg, and 3 DOF leg, and 4) TVAC testing for CHARLOTTE’s feet, radiator, and MVDC cable. The results of these experiments were included in CHARLOTTE’s final report, which was submitted to NASA’s BIG Idea Challenge. The lunar sandbox, while also expanding the lab’s environmental testing capabilities, is also being developed as an outreach piece, where the public will be able to control a RC car in the sandbox, as though they were driving on the lunar surface. This project is currently being worked on by a capstone group.
 Figure 1. CHARLOTTE in gravity harness in the lunar sandbox.
Figure 1. CHARLOTTE in gravity harness in the lunar sandbox.
 Figure 2. The test set-up for abrasion testing on the MVDC cable.
Figure 2. The test set-up for abrasion testing on the MVDC cable.
 Figure 3. Thermal cycling set-up of the 3 DOF leg
Figure 3. Thermal cycling set-up of the 3 DOF leg
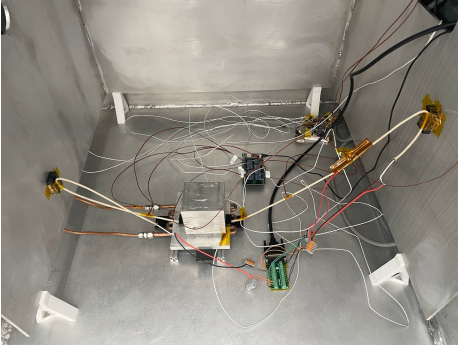 Figure 4. TVAC testing set-up of the MVDC cable.
Figure 4. TVAC testing set-up of the MVDC cable.
Comments